Most people have replaced their lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries with Lithium Iron Phosphate alternatives (LiFePO4 batteries) because of their many advantages. However, since LFP is a newer battery technology, many people still have questions regarding the management and maintenance of LiFePO4 batteries.
One of the common questions is, ‘can you overcharge LiFePO4 battery cells?’ This article will discuss what happens to a LiFePO4 battery when overcharged. By using the information provided in this article, you can significantly increase LiFePO4 battery life and reap the full benefits of LFP technology over a lead acid battery and other lithium-ion battery options.
What are LiFePO4 Batteries?

A LiFePO4 battery is a lithium battery that uses Lithium Iron Phosphate as the cathode material and graphite carbon as the anode. These batteries are significantly better than lead acid batteries and other lithium-ion batteries. Some of their benefits include longer lifespan, higher depth of discharge (DoD), better safety, and high capacity.
Can LiFePO4 Be Overcharged?
Can you overcharge a LiFePO4 battery? Yes. Does it cause any damage to it? Yes. Although LFP batteries are the safest batteries to overcharge, there are limits, as the sections below discuss.
What is Overcharging?
In short, overcharging occurs when the charging process continues after the battery cell has reached 100% charge. What happens if you overcharge liFePO4? Doing so can cause permanent damage to the battery pack. Most batteries have an inbuilt protection circuit to avoid this. It cuts off the supply of charging current once the battery’s voltage reaches its capacity.
Even when batteries have a protection circuit, there are often instances when this circuit isn’t configured correctly or gets damaged, resulting in excessive charging.
Each cell in a LiFePO4 battery has an inherent voltage of 3.65V. The good thing about LiFePO4 batteries is that you can charge lithium-iron-phosphate battery cells up to 4.2V. But increasing the voltage further can cause the organic electrolyte to break down.
What is the Common Reason for Battery Overcharging?
Battery overcharging occurs in one of the three following scenarios:
No Battery Protection System
A battery protection system includes a dedicated mechanism to prevent overcharging. However, cheaper batteries often don’t have this system – as it costs more. You should avoid buying batteries without this safeguard. Batteries with a protection system might cost slightly more initially, but they make up for it with significantly longer usable battery life.
Incorrectly Installed Battery Protection System
Non-branded batteries often have this problem because the battery protection system is set up incorrectly, so the system fails, and the battery gets overcharged and irreversibly damaged.
Battery Protection System Failure
Even if set up correctly, a battery protection system may still fail due to a technical fault. However, generally, you can avoid this possibility by using a Battery Management System (BMS).
What is a Battery Management System (BMS)?
A BMS is an electronic management system designed to protect a rechargeable battery. The system typically has several features:
- Overcharge protection circuit
- Short circuit protection
- Maintaining safe operation
- Monitoring data such as voltage, current, charge, cell health, coolant flow, and cell balance
- Smartly optimising the charging voltage
- Heating the battery in low temperatures
A BMS is not standard in all batteries. Only high-quality lithium-iron phosphate batteries, such as those provided by Eco Tree Lithium, come with this feature.
Is a Battery Management System Useful for a LiFePO4 Battery?
Yes, a BMS is an indispensable feature of lithium-iron phosphate batteries. High-capacity batteries such as LFP batteries are a costly investment. These batteries often operate in adverse conditions and experience over-discharging, overcharging, short circuits, or extreme temperatures. A BMS ensures optimal operation in these conditions.
Batteries that come without a BMS might be a cheaper option. However, without a BMS, lithium-iron phosphate batteries that could last for 10 to 20 years might only last for 3 to 5 years. Therefore, a BMS is always beneficial to protect your investment in a LiFePO4 battery.
What Happens If a LiFePO4 Battery is Overcharged?

The battery charger supplies more voltage to each cell than the specified nominal operating voltage range. As a result, the positive electrode material experiences lithium ions overflow. The negative electrode is unable to absorb a lot of these ions since it has exceeded its capacity. This situation leads to the formation of lithium dendrites, causing an internal short circuit.
This short circuit raises the temperature and begins to break down the electrode material, which can permanently reduce the lithium-iron-phosphate battery’s performance.
So what happens if you overcharge a liFePO4 battery? The following things will happen in this case:
Permanent Damage: Even if you overcharge the battery once, there will be permanent damage because once the decomposition reaction of internal electrode materials begins, the electrodes are unrepairable.
Loss of Capacity: The electrode damage due to the loss of some of its material subsequently reduces the storage capacity. As a result, the battery functions at a reduced capacity and provide limited use.
High Impedance: Overcharge damage not only reduces the battery’s capacity but will also reduce its charging rate and how efficiently it supplies the stored energy.
Faster Discharge: A better with reduced capacity will discharge faster. Whereas before being damaged, it may have supplied power for a day, it might now last for half of that or even less.
Higher Heating: Batteries that are damaged heat up at a higher rate. If the battery remains in an overcharged state for a long time, it can even lead to a fire.
Reduced Lifespan: Due to the permanent cell damage, the battery’s lifespan reduces. And if left in an overcharging state, the battery might not function at all.
Warning Signs of an Overcharged Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery
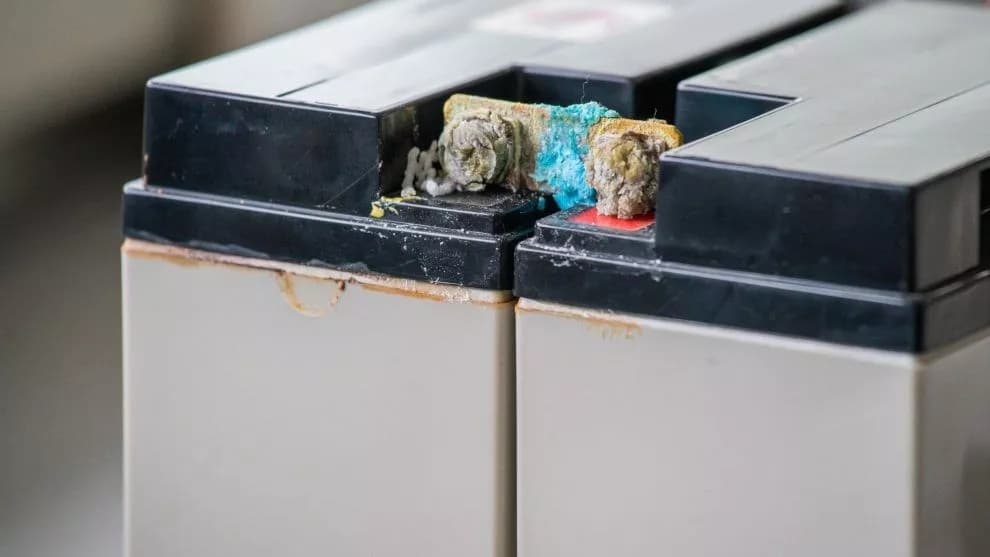

Many warning signs may occur when a lithium iron phosphate battery is overcharged. These signs include:
- Overheating of the battery
- Swollen battery
- Discolouration
- Unusual smell from the battery
These signs are not exclusive to overcharging and may also indicate other issues. Additionally, overcharging can occur even without exhibiting these signs. Therefore, a BMS is the best way to detect and prevent overcharging.
Can an Overcharged LiFePO4 Battery Be Repaired?
No, there is no possibility of battery repair in case of over-discharging or overcharging. This applies to lithium iron phosphate and other battery types. Excessive charging causes permanent and irreparable damage. The best advice is to contact the manufacturer and seek help.
What To Do If You Overcharge a LiFePO4 Battery?
If you overcharge lithium iron phosphate cells, you should act promptly to restrict the damage caused. The things to do are:
- Disconnect the battery charger immediately.
- Slowly discharge it with low current levels below 0.1C, such as 10A for a battery of 100Ah capacity. Discharge the cells enough to decrease the cell voltage to a normal range, such as 3.2V for lithium-iron phosphate batteries.
- If the battery cells have a pressure safety valve, open it. Not all cells have a safety valve. And the steps to release it can vary based on the battery. Refer to the battery manual for more details, or contact the manufacturer.
- It is good practice to do some testing cycles to evaluate the cell performance and how it has been affected by the overcharge. In the case of decreased performance, indicating cell damage, do not charge the cells repeatedly to full voltage. Charge them to around 80% to 90% of their capacity to eliminate further decomposition and damage.
LFP Battery Charging Guidelines
Lithium-iron phosphate batteries are the safest batteries on the market. It is easy to eliminate any possibility of overcharging by following the charging guidelines below.
- Optimal Temperature Range: Every battery has an optimal temperature range for charging and operating conditions. Make sure you charge the battery only in these optimal conditions. For lithium-iron phosphate batteries, the recommended safe temperature is between 0°C and 45°C (32°F and 113°F). When charging at higher or lower temperatures, there is no need for temperature compensation for voltage when charging a lithium-ion battery.
- Avoid Complete Charge and Discharge: Do not charge the battery to 100% capacity or discharge it to 0% to avoid the possibility of overcharging and over-discharging.
- Correct Battery Charger: Many users buy aftermarket chargers to save money rather than getting an authentic LFP charger. Poor-quality chargers can seriously degrade the battery since the charging voltage varies between chargers. Only use the charger recommended by the manufacturer. In addition, never use a lead acid battery charger to charge lithium batteries.
- Storage: Follow proper storage guidelines that come with the battery. For instance, some batteries should be charged or discharged to a certain level before storing them. With optimal; storage conditions for your liFePO4 batteries, they will work perfectly when needed again.
- Fast Charging: Fast charging may seem appealing, but it is never good for the battery’s health. The best way to charge the battery is slowly with the recommended charger. Fast charging provides high voltages to the battery, which can easily cause overcharging.
How to Know When a LiFePO4 Battery is Fully Charged?
It is easy to find out the charge level of a LiFePO4 battery at any time because the fully charged voltage of a lithium iron phosphate cell is 3.65 V. The normal cell voltage is 3.2 V, and the discharge cell voltage is 2.65 V. Therefore, you can ascertain whether the battery is in a fully charged or partially discharged state by checking the cell voltage of a lithium iron phosphate battery.
What is LiFePO4 Over-Discharging and How to Manage It?
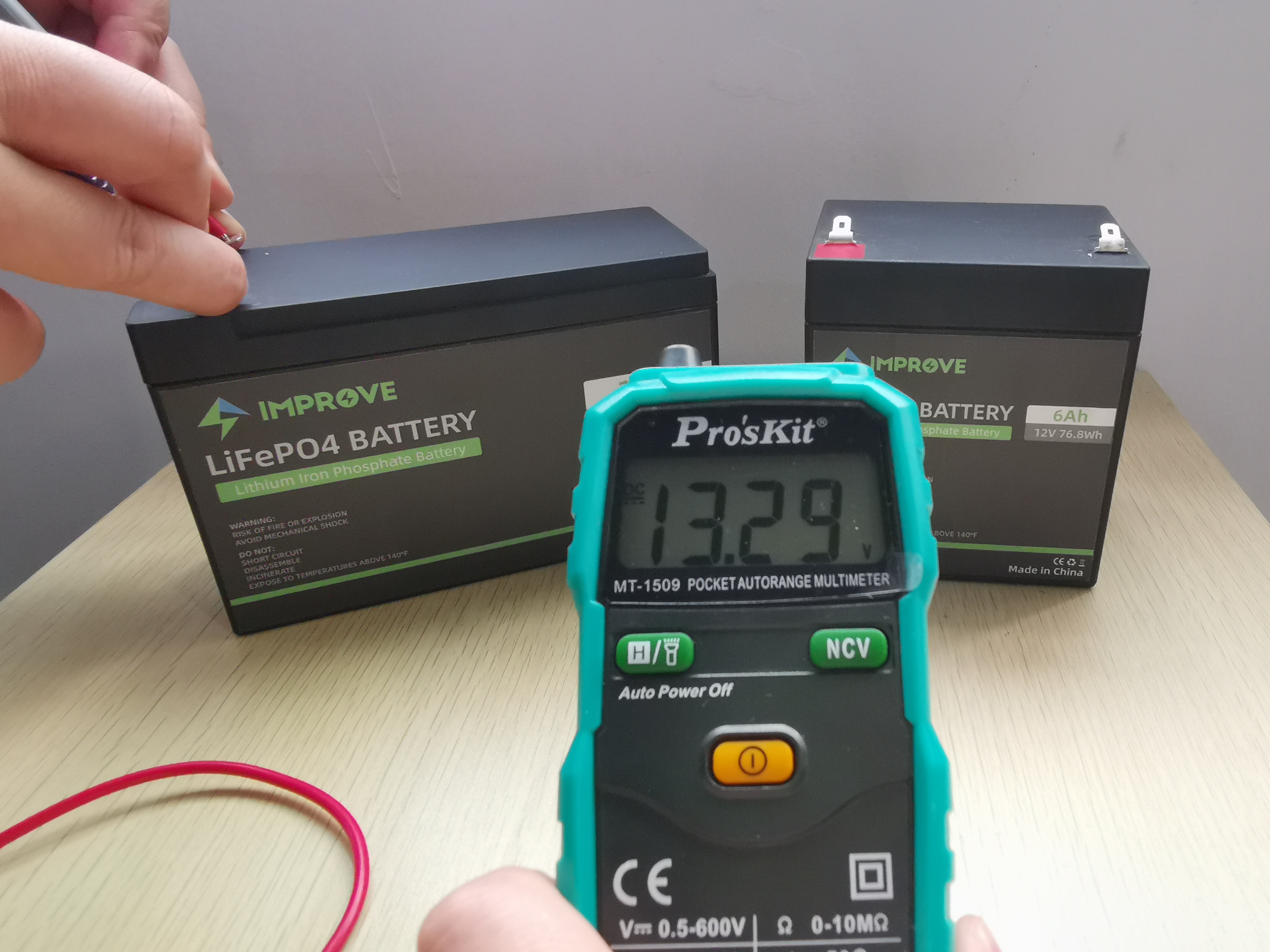

It is just as common to over-discharge lithium-iron phosphate batteries as overcharge them. The battery is 100% discharged, but an external load still tries to draw power from it. When you over-discharge lithium batteries, it causes the formation of dendrites similar to the overcharge process.
The Battery Management System (BMS) protects not just from overcharging, but also from over-discharge as well. When the battery capacity is at a dangerous low voltage, the BMS disconnects it, avoiding any further power draw from the battery.
Conclusion
Lithium iron phosphate is the safest among all lithium batteries, tremendously better than a lead acid battery. Even so, they are prone to the overcharge/over-discharge phenomenon, as all lithium batteries are. Therefore, it is advisable to take proper precautionary steps to avoid overcharging or over-discharging rather than dealing with a permanently damaged battery that will never recover its original charge-holding capacity again.